Navigating the Climate-Neutral Economy: A Practical Guide for Businesses

In today’s ever-changing business landscape, staying ahead of the curve is essential for long-term success. But what if we told you that the key to future-proofing your business lies in the climate-neutral economy?
The climate-neutral economy is not just a buzzword; it’s a fundamental transformation reshaping industries globally. This blog post will guide you through the crucial aspects of understanding, adopting, and thriving in this new era of business. We’ll explore the climate-neutral economy, the regulatory changes affecting businesses, the concept of carbon pricing, risk assessment, mitigation strategies, and real-world case studies from India.
Here’s what you can expect to learn:
- What is the climate-neutral economy and why is it vital?
- The impact of regulatory changes on businesses, with a focus on India.
- The concept of carbon pricing and its significance.
- Strategies for assessing and mitigating climate-related risks.
- Real case studies of Indian businesses successfully embracing climate neutrality.
As you read through this post, consider how your business can embrace climate neutrality and thrive in this changing world. We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments, join the conversation on social media, and subscribe to our blog for more insights on sustainable business practices.
In today’s ever-changing business world, staying ahead of the curve is paramount for long-term success. One of the most significant shifts we’ve witnessed is the growing importance of climate neutrality. It’s not just a trendy buzzword; it’s a fundamental transformation that’s reshaping industries and challenging businesses worldwide.
Don’t fret; we’re here to guide you through this journey, step by step.
Understanding the Climate-Neutral Economy
So, what is a climate-neutral economy? Simply put, it’s an economy where greenhouse gas emissions are balanced by removing an equivalent amount of greenhouse gases from the atmosphere. According to the Inter-governmental panel on Climate Change (IPCC), climate neutrality, also known as net-zero emissions, means that “the balance between anthropogenic emissions by sources and removals by sinks of greenhouse gases (GHGs) in the atmosphere is zero.” This equilibrium is crucial to combating climate change, which has wide-ranging consequences for businesses. Rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and changing consumer preferences are just the tip of the melting iceberg.
This equilibrium is crucial to combating climate change, which has wide-ranging consequences for businesses. Rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and changing consumer preferences are just the tip of the melting iceberg.
In 2015, the world came together to address climate change through the Paris Agreement. Signed by 196 parties, including India, this landmark agreement aims to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels and to pursue efforts to limit it to 1.5 degrees Celsius. The agreement outlines the commitment of nations to regularly report on their emissions and efforts to reduce them.
Regulatory Changes and Their Impact
Regulations are a big part of the climate-neutral shift. Governments worldwide are enacting laws to curb emissions, and India is no exception. Understanding these changes and their impact on your business is critical. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines and a tarnished reputation.
For example, the Indian government introduced the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) in 2008. This comprehensive plan outlines eight national missions to address climate challenges. Key aspects of the NAPCC include:
- The National Solar Mission, promoting the use of solar energy.
- The National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture, focusing on climate-resilient agriculture practices.
- The National Mission for Enhanced Energy Efficiency, targeting energy conservation.
- The National Water Mission, aiming for efficient water resource management.
These missions provide businesses with clear avenues for aligning their operations with national climate goals.
Carbon Pricing Mechanism: Understanding the Costs
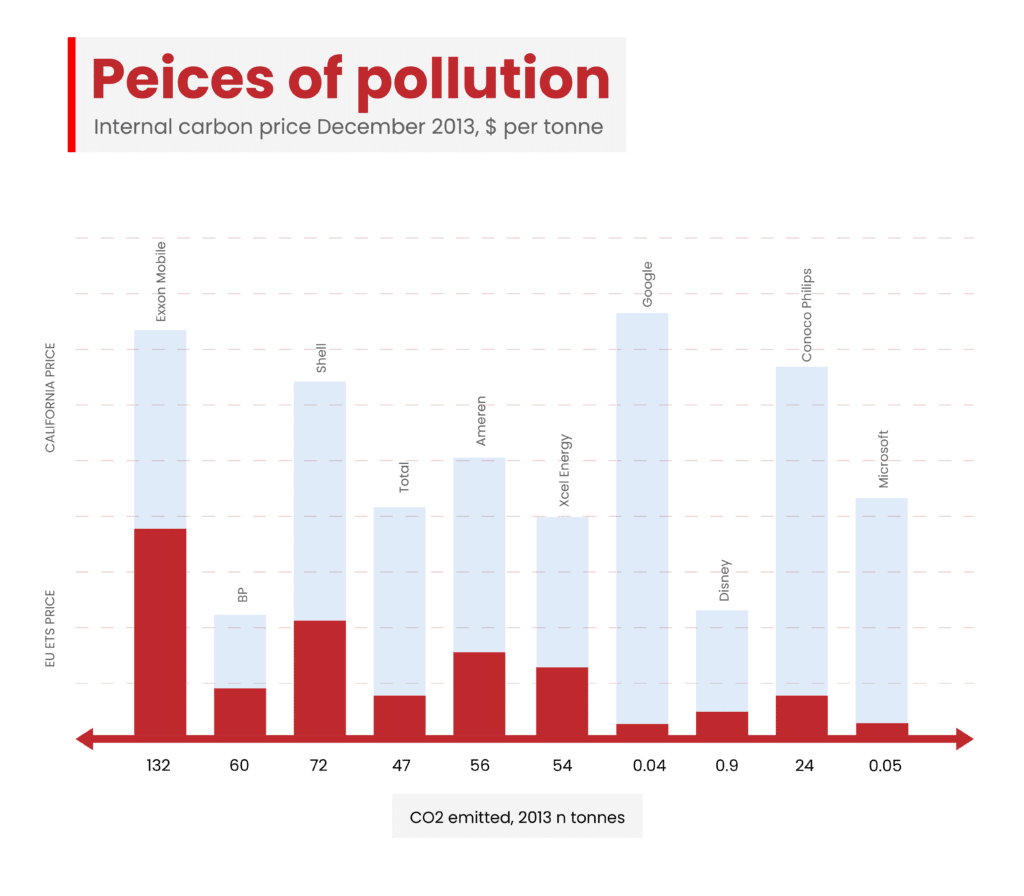
The concept of carbon pricing is integral to climate neutrality. Essentially, it places a price on carbon emissions to motivate businesses to reduce their carbon footprint. In the European Union, for instance, companies emitting above their allocated limits are required to purchase carbon allowances.
Internal carbon prices set by various US corporations (The Economist, April 2017, Jeremy Ian)
Here’s how carbon pricing works:
- Carbon Allowances: Governments set a limit (cap) on the total amount of carbon dioxide emissions a particular sector can emit. This limit is often reduced over time to align with emission reduction goals.
- Allowance Allocation: Businesses within the sector are allocated a specific number of carbon allowances based on their historical emissions or other criteria.
- Trading System: Businesses can buy and sell these allowances in a carbon market. Those that reduce emissions below their allocated allowances can sell their surplus allowances to others that exceed their limits.
- Carbon Price: The price of carbon allowances is determined by supply and demand in the market. If emissions are high and allowances are scarce, the price rises, creating a financial incentive for businesses to reduce emissions.
For instance, let’s say an Indian manufacturing company receives 10,000 carbon allowances for a year. If they emit 12,000 metric tons of CO2 and the current carbon price is $50 per metric ton, they would need to purchase 2,000 additional allowances, resulting in a cost of $100,000.
This cost not only serves as a financial penalty for exceeding emissions limits but also encourages businesses to invest in emission reduction measures, such as energy efficiency upgrades or renewable energy adoption.
Climate-Neutrality related Risk, and Mitigation
Environmental Risk Assessment
Environmental risk assessment involves evaluating how environmental factors can affect your business operations. In India, changing climate patterns, such as irregular monsoons or increased cyclone frequency, can have severe repercussions for businesses. For instance, a textile manufacturer located in a region prone to flooding may face supply chain disruptions, damage to infrastructure, and increased operational costs due to extreme weather events.
Building a Climate-Resilient Supply Chain
Creating a climate-resilient supply chain is paramount. One of the key strategies for businesses is diversifying suppliers to reduce dependence on a single region or source. Let’s take the example of an Indian electronics manufacturer. They expanded their supplier base to different states in India, mitigating the risk of supply disruptions caused by localized climate-related events. This proactive approach not only safeguards against risks but also ensures uninterrupted production.
Insurance in a Changing Climate
Insurance plays a vital role in managing climate-related risks. In India, where extreme weather events are becoming more frequent, securing adequate insurance coverage is essential. Suppose you run a logistics company with a fleet of vehicles. As climate-related events like heavy rainfall or cyclones become more common, the risk of vehicle damage and business interruptions rises. Adequate insurance coverage can provide financial protection in such situations.
In-Depth Risk Mitigation Strategies
Let’s dive deeper into risk mitigation strategies:
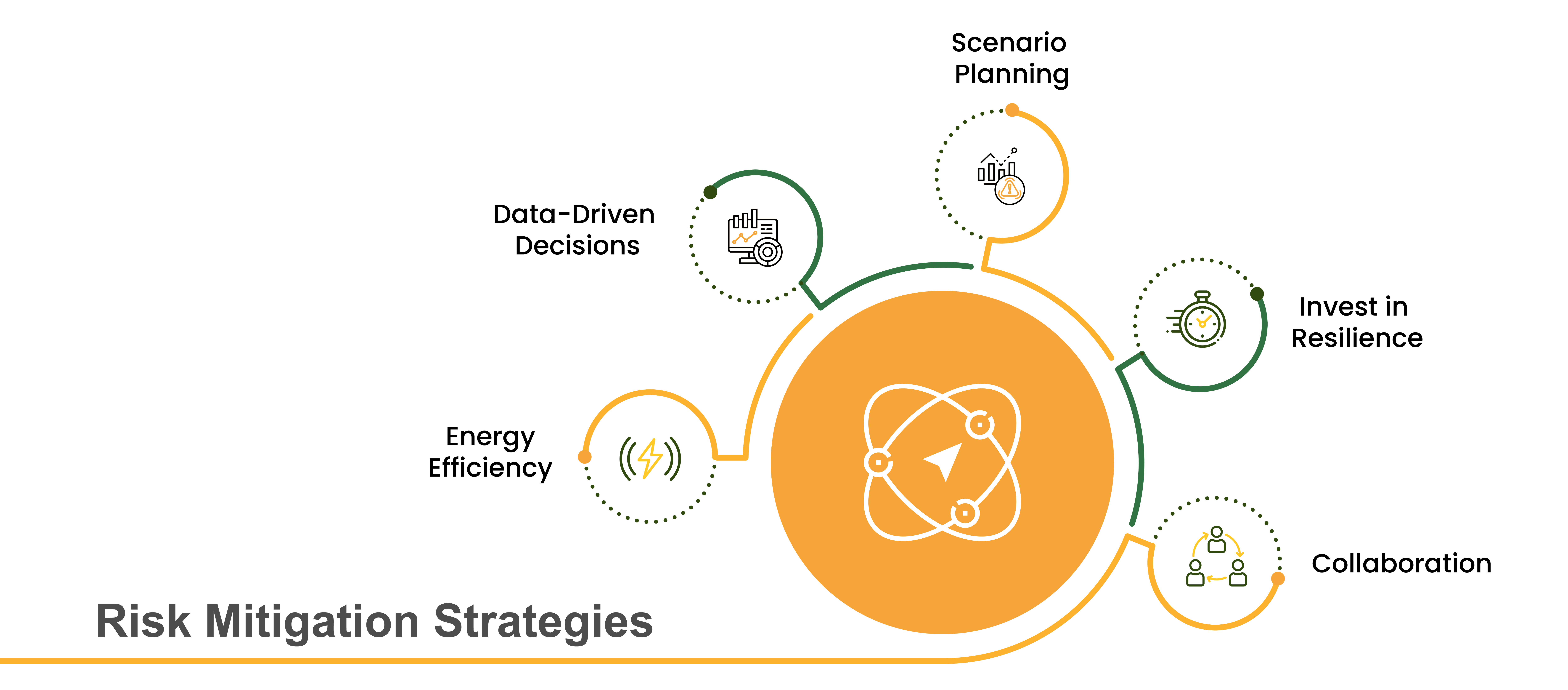
Energy Efficiency
Implementing energy-efficient practices reduces operational costs and carbon emissions. A textile mill in India, for instance, upgraded its machinery to improve energy efficiency, resulting in both cost savings and reduced environmental impact. Efficiency
Data-Driven Decisions
Investing in data collection and analysis helps businesses make informed decisions. For instance, a major retail chain in India uses data analytics to optimize inventory management, reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions.
Scenario Planning
Developing scenarios for climate-related risks is crucial. An automobile manufacturer in India uses scenario planning to prepare for potential disruptions in its supply chain due to extreme weather events.
Invest in Resilience
Strengthening infrastructure and assets ensures they can withstand climate-related stressors. A telecommunications company in India invested in resilient infrastructure to ensure uninterrupted service during extreme weather conditions.
Collaboration
Partnering with other businesses and organizations fosters knowledge sharing and collective resilience. A group of Indian manufacturers collaborates on sustainability initiatives, sharing best practices and resources.
By understanding and implementing these strategies, businesses in India and across the globe can effectively mitigate climate-related risks, reduce costs, and position themselves for long-term success in a climate-neutral economy.
Case Studies from India on Climate Neutrality

Green Farms: Agriculture and Climate Neutrality
Consider the case of “Green Farms”, an agri-business in India. Faced with increasingly varying weather patterns, Green Farms adopted climate-neutral practices. They implemented precision agriculture techniques, optimized water usage, and introduced renewable energy sources on their farms. As a result, they not only reduced their carbon emissions but also improved crop yields and resilience to climate-related risks. This innovative approach not only secured their sustainability but also attracted environmentally conscious consumers and investors.

EcoFab: Sustainable Manufacturing in India
Let’s examine a real-world case of a manufacturing company in India that embraced climate neutrality practices. “EcoFab India” is a textile manufacturer based in Tamil Nadu. Faced with increasing environmental regulations and changing consumer preferences, they embarked on a sustainability journey.
Reducing Energy Consumption
EcoFab India invested in state-of-the-art machinery that significantly reduced energy consumption in their textile production process. They adopted energy-efficient lighting systems and optimized their heating and cooling systems. As a result, their energy bills dropped by 25%, directly impacting their bottom line.
Water Recycling and Conservation
In a region known for water scarcity, EcoFab India implemented a comprehensive water recycling and conservation system. They reduced water consumption by 40% and saved significantly on water costs. This approach not only reduced their environmental impact but also made them resilient to water-related risks.
Supply Chain Sustainability
EcoFab India engaged with local farmers to source organic cotton, reducing their reliance on water-intensive conventional cotton farming. This move aligned with sustainability goals while strengthening their supply chain by supporting local communities.
Carbon Offsetting
To address the remaining carbon emissions, EcoFab India invested in afforestation projects in collaboration with environmental organizations. This not only allowed them to achieve carbon neutrality but also contributed positively to the environment.
Consumer Trust and Market Expansion
As consumers became increasingly eco-conscious, EcoFab India’s sustainability initiatives resonated with their target market. They noticed a surge in demand for their sustainable textile products both domestically and in international markets. This newfound consumer trust translated into increased sales and revenue.
Government Support
The Indian government’s focus on sustainability and renewable energy aligned with EcoFab India’s goals. They took advantage of government incentives and subsidies for clean energy adoption, further reducing their operational costs.
This case study of EcoFab India exemplifies how businesses in India can thrive by adopting climate-neutral practices. Their journey not only reduced costs and environmental impact but also opened up new market opportunities. Their commitment to sustainability became a selling point, attracting environmentally conscious consumers both at home and abroad.
As you can see, practical steps taken by businesses can lead to remarkable outcomes. The key takeaway is that understanding and embracing climate neutrality is not just about compliance; it’s about seizing opportunities for growth and resilience in a changing world.






