Groundwater pollution(or contamination), occurs when unwanted substances called pollutants, seep from the land surface into the groundwater during the groundwater recharge process.
As per data available, more than 12 million people in India were affected by Arsenic in 2019, which is a lethal groundwater pollutant. Drinking arsenic-rich water over a longer period may cause cancer, high blood pressure, diabetes, and diseases of blood vessels. Another report of 2018 states that major toxins like nitrate, fluoride, iron, and heavy metals like lead, cadmium, and chromium are exceeding their permissible limits in many districts of India.
Identifying and knowing the cause of any problem is the key to its remediation. So, this article will explain some of the major causes of groundwater pollution. And we’ll also look into some of the ways to prevent groundwater pollution.
Also read: Latest CGWA Guidelines on Groundwater Monitoring
Major Causes of Groundwater Pollution
The sources (or causes) of groundwater pollution can be landfills, effluents released from industries or wastewater treatment plants, leakage from sewers, petrol filling stations, or fertilizers/pesticides used in agriculture.
Interestingly, the cause of groundwater pollution can also be native(natural) due to arsenic or fluoride contamination.
1. Naturally Occurring(Geogenic) Chemicals
Compounds of arsenic and fluorine formed under certain conditions in the aquifers are the major sources of Geogenic(natural) groundwater pollution.
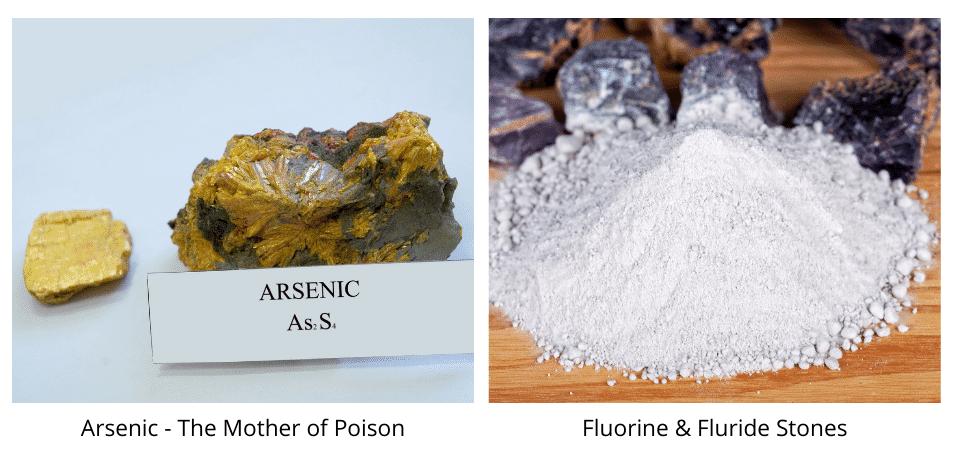

Arsenic is a naturally occurring metal present in the earth’s crust. In its organic form, it’s poisonous and quite lethal in nature. It gets dissolved in groundwater due to the anaerobic conditions produced by organic matter present inside the aquifers. Due to the microbial decomposition of the organic matter, the oxides of iron are released into the groundwater aquifers. These iron oxides then react with the arsenic and produce arsenic compounds – arsenite and arsenate, the former being more toxic than the latter.
The second major geogenic pollution occurs due to the compounds of fluoride found in the groundwater. These are present in aquifers that lack Calcium inside them. The permissible limit of fluoride concentration in groundwater is 1.5 mg/l as per WHO Guidelines since 1984. More than this may result in “dental fluorosis” a condition characterized by hypomineralization of the tooth enamel.
2. Poor Sanitation Systems
Poor sanitation systems imply a drinking water source, like water well built too near to pit toilets or septic tanks. They can pollute the groundwater making it quite unfit for potable purposes.
Water from the sanitation systems can infiltrate the unsaturated zone and enter the aquifers.
The challenge that lies here is the appropriate distance between the septic tanks and the point where water can be extracted can’t be determined easily. This is because it depends upon local hydrological conditions and thus, varies from place to place. Although the pathogens die in between the time travel before they reach the aquifer when water seeps into the ground, this process is quite complex in itself as it depends upon aquifer type, soil type, and other environmental factors. So this natural water treatment process, also known as SAT, doesn’t guarantee a pathogen-free liquid entering into the aquifer.
3. Improper Sewage Dispossal

Poorly treated sewage water disposed on the ground surface or local water bodies is also a reason for groundwater pollution. This problem arises in the areas where there is a poor infrastructure of sewage treatment plants or poorly maintained sewer systems.
Also, if there are micro-pathogens like hormones, pharmaceutical residues and other micro-contaminants that are found in urine or feces is present in the sewage, then even the conventional treatment plants may not be able to remove such impurities. An example of this was found in several locations of Germany where pharmaceutical residues of the order of 5-ng/L were present in groundwater.
4. Excessive Use of Fertilizers and Pesticides
Pesticides and commercial fertilizers, or even natural fertilizers like manure are nitrogen-based compounds that can introduce nitrates into the groundwater and pollute it. This is mainly because only a certain portion of the nitrogen is used by plants and the rest may get either washed off to enter water bodies or seep into the ground polluting the aquifers.
Also, animal manure may also contain pharmaceutical pollutants if the animals were subjected to veterinary treatments.
5. Leakage from Industrial Pipes and other industrial releases
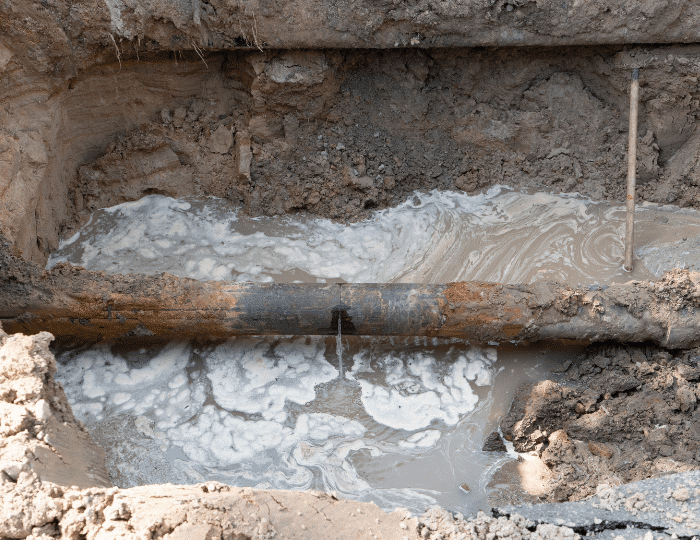

Leakage from the underground industrial pipes and oil tanks is also causing groundwater pollution around industrial areas.
Mining of ore and metal may introduce toxic metals like arsenic into the groundwater due to improper waste disposal. The acidic nature of their waste also helps other harmful metals to get easily dissolved into it and seep into the aquifers.
Similarly, gasoline stations may cause groundwater pollution if their storage tanks leak and release benzene and other low-density compounds into the ground. These substances will float on the top surface of the water table due to their lower densities than water and will make them unfit for household use.

6. Over pumping of groundwater
Pumping groundwater aggressively may release arsenic into the water and also cause land subsidence(sudden sinking of land).
Arsenic is mainly present in the clayey layer of the underground surface and little of it seeps into the water while groundwater is pumped. But if overdone, a substantial amount may get entered into aquifers due to the high hydraulic gradient created.
7. Improper Landfill practices
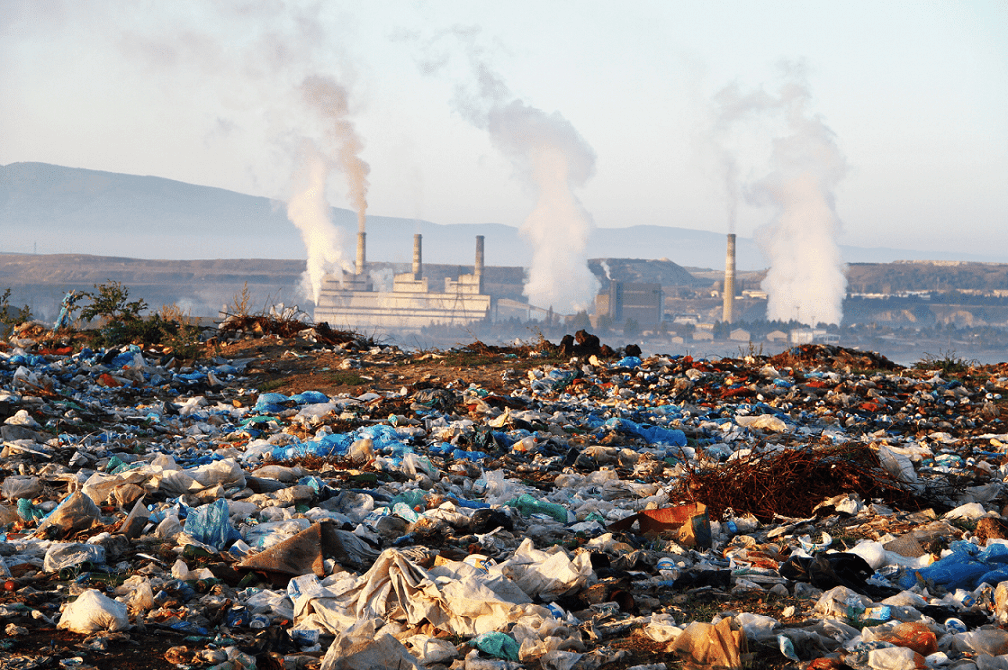

One of the major examples of groundwater pollution due to landfill leachate is the Love Canal, an aborted canal project near Niagara Falls, New York. In 1978, the area started reporting quite a number of cases of cancer and birth defects in the population residing around. The investigation followed after traced it to the organic/inorganic toxic contaminants leaching into the groundwater from the industrial landfill present in the area.
Ways to Prevent Groundwater Pollution
There exists regulatory requirements such as if any company extracts more than 10 cubic meters of groundwater a day, you must get an NOC from CGWA. Some ways to prevent groundwater pollution-
Also read: CGWA guidelines for individual domestic consumers extracting groundwater for swimming pools
1. Using the Precautionary Principle
The precautionary principle states that “where there are threats of irreversible damage, lack of full scientific certainty shall not be used as a reason for postponing cost-effective measures to prevent environmental degradation“.
This principle was adopted at Rio Declaration and is mentioned in their 15th principle as a tool to combat groundwater pollution. And this also one of the Six Principles of the European Union(EU) Water Policy.
2. Monitoring Quality of Groundwater through a telemetry system
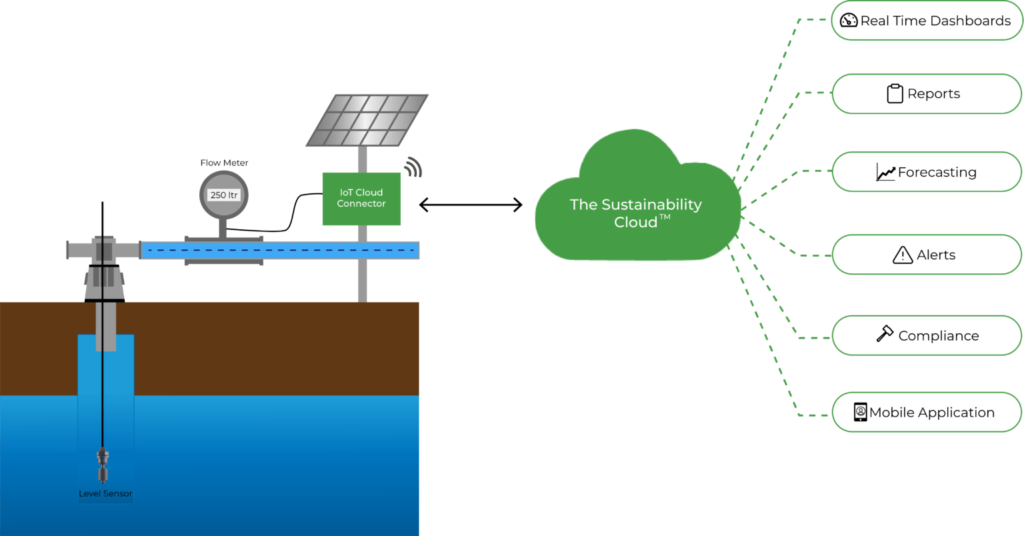
Groundwater quality monitoring should be done, especially by industries to measure groundwater parameters like pH, flow rate, TSS, water level, etc. Prompt action should be taken if any problem is observed.
3. Land Zoning or Marking
Zoning or marking land areas to ensure a better focus on specific areas for preventing groundwater pollution is another strategy to adopt. This measure of creating land-use maps has been used by many nations around the world.
There are essentially two types of zoning maps – Aquifer vulnerability maps and source protection maps.
Aquifer vulnerability maps are created taken into account that certain aquifers are more susceptible to groundwater pollution than others, especially shallow aquifers. This is because there are fewer layers that act as filters between the land surface and the aquifer layer that holds water.
Source protection maps are formed to protect individual water sources, like wells or springs. If there is an adequate travel time between biodegradable pollutant source and groundwater source, then the pollutants get eliminated due to the adsorption or filtration process along its way. So the source protection maps are created to specify radial areas around a water source where activities that can cause pollution need to be omitted.
4. Via Statuary Regulations
Government regulations have a key role in tackling the issue of groundwater pollution.
In India, the statuary body constituted under section 3 of the Environmental (Protection)Act, under the name CGWA(Central Groundwater Authority) is responsible for accounting for groundwater developments across the country. As per the latest guidelines issued by CGWA, it’s mandatory for various industries meeting certain criteria need to install a groundwater monitoring telemetry system and provide the report to CGWA.
5. Educating Others

Creating awareness around the importance and an urgent need to take steps for groundwater prevention pollution will also help in combating the issue.
Groundwater is a commodity used by everyone. So the onus to protect it from contaminants and its scarcity for the present & future generations lie on each and every individual on the face of the earth. Each and every individual can play a role by taking small but effective steps like not wasting water in the house or workplace, using fewer plastics, and proper disposal methods.




